Discover the intriguing phenomenon of solo reproduction in a female stingray at a US aquarium. Explore the mystery behind US Female Stingray’s Solo Reproduction.
In a remarkable twist of nature, Charlotte, a resident stingray at a North Carolina aquarium, has defied expectations by displaying signs of pregnancy, despite the absence of any male stingrays in her enclosure. This captivating phenomenon has left marine experts and enthusiasts alike pondering the mysteries of reproduction in aquatic creatures.
Table of Contents
Discovery of Charlotte’s Pregnancy
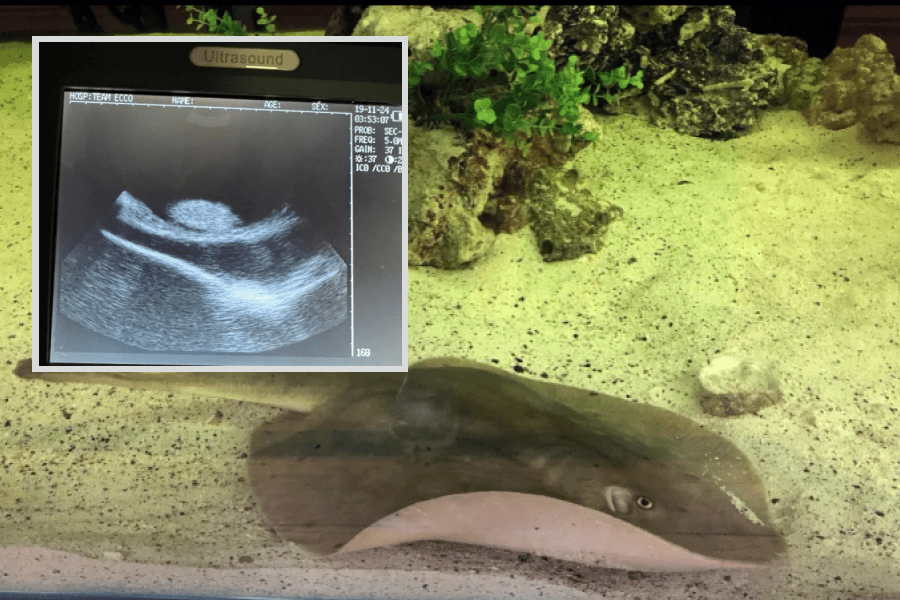
The intrigue began in September when the staff at the Aquarium and Shark Lab by Team ECCO noticed Charlotte’s abdomen swelling. Initially, concerns arose over the possibility of cancer, prompting immediate attention and investigation. However, subsequent ultrasounds revealed a surprising revelation – Charlotte was carrying multiple pups within her.
Exploring Possible Explanations
The revelation of Charlotte’s pregnancy sparked intense speculation among marine biologists and aquarium staff. Two primary hypotheses emerged to explain this perplexing occurrence:
Rare Reproductive Strategy
Parthenogenesis, a phenomenon observed in certain species, involves the development of embryos from unfertilized eggs. In Charlotte’s case, this theory suggests that she may have undergone parthenogenetic reproduction, resulting in offspring genetically identical to herself. While parthenogenesis is relatively rare in stingrays, it has been documented in other species and cannot be ruled out as a potential explanation.
Asexual reproduction, a fascinating phenomenon observed extensively among marine creatures, including stingrays, has garnered significant attention in the realm of biological research. Studies have illuminated the remarkable ability of certain species, such as stingrays, to engage in asexual reproduction when conventional mating opportunities are scarce or absent.
Dr. April Smith, the esteemed executive director of the North Carolina Science Trail, eloquently elucidates the concept of parthenogenesis in her insightful blog post. Parthenogenesis entails the asexual reproduction of an organism, wherein a female organism produces embryos without the need for fertilization by a male counterpart. This extraordinary reproductive strategy results in offspring that are typically genetically identical to the mother and predominantly female in composition. Parthenogenesis manifests in environments where males are absent, such as controlled settings like zoos or aquariums, as well as remote natural habitats like the depths of the ocean. This mechanism serves as a vital survival strategy, facilitating the perpetuation and preservation of species in challenging or isolated environments.
Interspecies Mating with a Male Shark
Another intriguing possibility revolves around the introduction of a male shark into Charlotte’s environment. In July, two young white-spot bamboo sharks were relocated to her tank, raising the prospect of interspecies mating. Bite marks observed on Charlotte’s fins, reminiscent of those associated with shark mating behavior, lend credence to this theory. If confirmed, this would represent a remarkable instance of cross-species reproduction within the aquarium setting.

Significance of Charlotte’s Pregnancy
Beyond its inherent fascination, Charlotte’s pregnancy offers valuable insights into the reproductive biology of stingrays and the broader field of marine science. By unraveling the mechanisms behind her unexpected gestation, researchers hope to gain a deeper understanding of reproductive strategies, genetic diversity, and species interactions in aquatic ecosystems.
Anticipation and Future Developments
As Charlotte’s due date approaches, anticipation mounts within the aquarium community. The impending arrival of her pups holds the promise of discoveries and further enriches our appreciation for the wonders of marine life. DNA testing will be conducted post-birth to ascertain the genetic composition of the offspring, shedding light on their parentage and potential implications for future research.
The enigmatic pregnancy of Charlotte the stingray serves as a testament to the boundless complexity and intrigue of the natural world. As scientists and enthusiasts continue to unravel its mysteries, one thing remains certain – Charlotte’s story exemplifies the remarkable resilience and adaptability of marine life, captivating hearts and minds alike in its wake.
Also see: Colombia’s Hippo Crisis: Government’s Wildlife Safeguard